It really hurts to have a lump behind your knee. Also known as baker’s cyst. This article will provide you with the symptoms, causes and treatment useful when having a lump behind your knee. In most cases lump behind the knee will be as a result of an underlying medical condition such as arthritis or cartilage tear. It’s advised you see your doctor as soon as possible to rule out on such causes.
A lump behind the knee, also called baker’s cyst or popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of the knee. It’s caused when the tissue behind the knee joint becomes swollen and inflamed. The swelling and inflammation can cause; pain in the knee and calf, a build-up fluid around the knee and at times locking in the knee joint. However, sometimes it might not cause any symptoms other than the fluid swelling behind the knee.
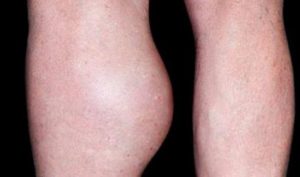
The most effective relief comes from treating the underlying problem. Surgery is at times needed to drain the cyst. In rare cases, the lump can burst (rupture), resulting in fluid leaking down into your calf. This can cause sharp pain, swelling and redness in your calf.
Lump behind knee baker’s cyst meaning
A lump behind the knee also called baker’s cyst or at times popliteal cyst. It is the swelling on the back of the knee caused by the build-up of fluid inside sacs called bursa between the two heads of the calf muscles. The symptoms are usually mild, except in rare situation when the cyst bursts or extends down into the calf muscles.
The entire knee joint is enclosed inside a tough capsule lined with a membrane and filled with a lubricating synovial fluid. An extra sacs known as bursa helps cushion the joint and help reduce the friction between tissues caused by movement. When the knee produces too much synovial fluid, the excess fluid causes the bursa behind the knee to expand and bulge. Common causes of Baker’s cyst include arthritis, infection, torn knee cartilage and other knee injuries.
The cyst can vary in size from a very small cyst to a large cyst that is a number of centimeters across. Rarely, a Baker’s cyst can develop behind both knees at the same time.
Lump behind knee images, pictures
In this page we have inserted images or pictures showing knee lumps. This is to help you understand more to help you identify with your symptoms.
Lump behind knee causes
As mentioned earlier, lump behind the knee could be as a result of an underlying medical cause. It is advised you see your doctor as soon as possible to rule out on the possibilities of such conditions. Otherwise common causes would include:
1. Tumor/ knee cancer
Cancer starts when cells in the body starts to grow out of control. Knee cancer has the potential to spread and invade other parts of the body. It is good to note that not all tumors are cancerous. Having a lump behind knee would be a good symptom of knee cancer. It is good to see your doctor for early treatment to avoid spreading of the cancer to other parts of your body.
The initial symptoms of knee cancer would include pain, often around the knee, especially in tumors on the tibia or femur. The pain typically worsen overtime and is not related to the time of day. Swelling and tenderness typically occur late in the course of osteogenic sarcoma (an aggressive cancerous tumor in the born). This is gradually causes a lump behind the knee.
Treatment for knee cancer depends on the type of cancer, how far it has spread and your general health. The main treatment however include;
- Surgery, done especially if the cyst is very large or painful and other treatments have not worked. At times a keyhole method is used to close of the connection between the baker’s cyst and the knee joint. The cyst may also be removed at times using open surgery. surgery might help treat an underlying problem for example, repairing a meniscal tear
- Chemotherapy, this is done with medicine to kill the cancer cells, by damaging them so they can’t reproduce and spread. It is used if a cancer has spread or there is a risk that it will.
- Radiotherapy, this is the treatment of cancer involving high-energy radiation. It commonly used to tear the cancer. It would also work to treat other condition such as thyroid disease and some blood disorders.
Apart from the above medical treatment procedure, home remedies that might be of help to you would include consumption of broccoli, grapes, ginseng, myrrh, green tea, aloe Vera, lycopene, mushroom and soybeans in either direct or indirect form.
2. Lump behind knee after meniscus surgery
A meniscus tear is a common injury to the cartilage that stabilizers and cushions the knee joint. Treatment of such through surgery could cause the development of a lump behind knee. When the knee produces too much synovial fluid, the excess fluid causes the bursa behind the knee to expand and bulge causing a cyst.
Your doctor may recommend that you do not move your knee more than absolutely necessary after surgery. A bedrest is advised before you can resume daily activity. A physical therapy should begin right away after surgery. But heavy stresses, such as running and squats, should be postponed for some months.
3. Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammation of one or more of your body joints. Pain, swelling and stiffness are the primary symptoms. It is particularly common in the knee. Although there is no cure for arthritis, there are many treatment options available to help manage pain and keep you staying active. A surgery might help in treating a lump behind knee caused by arthritis. It advised you see your doctor as soon as possible.
A knee joint affected by arthritis may be painful and inflamed. Generally, the pain develops gradually over time, although sudden onset is also possible. There are other symptoms, as well:
- The joint may become stiff and swollen, making it difficult to bend and straighten the knee.
- Pain and swelling may be worse in the morning, or after sitting or resting.
- Vigorous activity may cause pain to flare up.
- Loose fragments of cartilage and other tissue can interfere with the smooth motion of joints. The knee may “lock” or “stick” during movement. It may creak, click, snap or make a grinding noise (crepitus).
- Pain may cause a feeling of weakness or buckling in the knee.
Many people with arthritis note increased joint pain with rainy weather.
4. Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood cell tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cells) signs and symptoms might include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, itching and feeling tired. The enlargement are usually painless. The popliteal lymph nodes, embedded in the fat contained in the popliteal fossa, sometime referred to as ‘knee pit’ this result in a lump0 behind the knee once they became enlarged and start to swell.
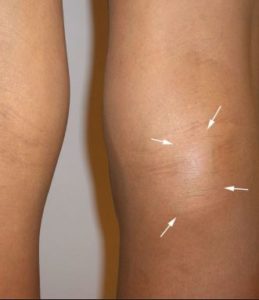
There exist many types of treatment. But your treatment choices depend on three main things,
- The type of lymphoma you have
- The stage of your lymphoma
- You general body health.
Treatment would include;
- Biologic therapy, this treatment increases your body ability to fight cancer. It does this by giving a boost to your immune system.
- Chemotherapy, this treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells and reduce the size of the cancer tumors. This drugs affect healthy cells and causes side effects like hair loss or mouth sores.
- Radiotherapy, this treatment uses high energy x-rays to kill cancer cells, the treatment often takes place in the part of your body the lymphoma is located.
- Transplant, high doses of chemotherapy destroys the lymphoma cells and your bone marrow, which develops blood cells. To avoid this some immature cells that will grow up into red blood cell, white blood cell and platelets (stem cell) maybe taken before chemotherapy, then translated back into the body. They will then find their way to the bone marrow and restore it.
5. Lump behind knee baker’s cyst
Lump behind the knee or baker’s cyst also known as popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of your knee. It is cause when the tissue behind the knee joint becomes swollen and inflamed. The swelling and inflammation can cause:
- pain in the knee and calf
- a build-up of fluid around the knee
- occasional locking or clicking in the knee joint
However, sometimes a Baker’s cyst may not cause any symptoms other than the fluid-filled swelling at the back of the knee.
In rare cases, a Baker’s cyst can burst (rupture), resulting in fluid leaking down into your calf. This can cause sharp pain, swelling and redness in your calf.
Baker’s cyst symptoms
The most common symptoms of baker’s cyst include the following:
- Mild to severe pain.
- Stiffness.
- Limited range of motion.
- Swelling behind the knee and calf.
- Bruising on the knee and calf.
- Rupturing of the cyst.
You should see your doctor as soon as you notice the symptoms above to advice on the best form of treatment.
Knee cyst treatment
Treatment for a knee cyst will depend on a variety of reasons ranging from how sever the symptoms are, how long the cyst has been, how big the cyst is and the causes of the cyst. You need to see you doctor to advice on the best form of treatment. Treatment may include:
- Fluid drain
- Physically therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- surgery
Baker’s cyst aspiration
Baker’s cyst aspiration means removal by suction of the fluid and cells through a needle. Your doctor will insert a needle into the swelling and use an ultrasound to help guide the needle to the correct place. They will then drain the fluid from the knee joint. However, it may not be possible to aspirate long-term (chronic cysts) because they’re made of jelly
Baker’s cyst removal surgery
Surgically removing a Baker’s cyst isn’t easy because unlike other types of cyst, they don’t have a lining. Surgery may be needed to repair your knee joint if it’s significantly damaged as a result of an injury or a condition such as osteoarthritis. A type of keyhole surgery called arthroscopy is usually used. The surgeon will use an instrument called an arthroscope to look inside your knee joint. Small surgical instruments can be used alongside the arthroscope to repair any damage.
6. Infection
Lump behind the knee as a result of infection is mainly caused by septic arthritis, that is, (joint inflammation caused by a bacterial infection). Septic arthritis also known as infectious arthritis, is usually caused by bacteria, or fungus, or a virus. Typically, septic arthritis affects one large joint, less frequently it might affect both joints.
It is usually caused by bacteria that spread through the blood stream from another area of the body. It can also be caused by a bacterial infection from an open wound or an opening from a surgical procedure, such as a knee surgery, the bacteria may include haemophilus influenza, staphylococcus and streptococcus. This bacteria enters the bloodstream and infect the joint causing inflammation and pain.
Fungi that can cause arthritis include Histoplasma, coccidiomyces, and blastomyces. Other infections, such as those caused by viruses and fungi, can also cause arthritis. Viruses include:
- Hepatitis A, B, and C
- Parvovirus B19
- Herpes viruses
- HIV (AIDS virus)
- HTLV-1
- Adenovirus
- Coxsackie viruses
- Mumps
7. Torn knee cartilage
Knee cartilage damage is a common injury. Cartilage is a tough, flexible tissue found throughout the body. It covers the surface of joints, acting as a shock absorber and allowing bones to slide over one another. The damage could be as a result of a sudden injury, such as sport activity or gradual wear and tear (osteoarthritis). Minor cartilage injuries may get better on their own within a few weeks, but more severe cartilage damage may eventually require surgery.
Symptoms of cartilage damage in a joint include:
- joint pain – this may continue even when resting and worsen when you put weight on the joint
- swelling – this may not develop for a few hours or days
- stiffness
- a clicking or grinding sensation
- the joint locking, catching or giving way
8. Gout
Gout is characterized by recurrent attacks of inflammatory arthritis. It is caused when the level of uric acid in the blood rise until it becomes excessive (hyperuricemia), causing urate crystals to build up around the joint. This causes inflammation resulting into a lump behind the knee. The cause is a combination of diet and genetic factors. It occurs more commonly in those who eat a lot of meat, drink a lot of beer, or are overweight.
Treatment for gout includes pain relief medication to help you cope with gout attack, as well as medication and lifestyle changes to prevent further attacks. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are usually recommended as the first treatment for gout. They work by reducing pain and inflammation during an attack. NSAIDs used to treat gout include naproxen, diclofenac and etoricoxib.
Certain lifestyle changes can also help reduce your risk of experiencing further attacks of gout, including:
- avoiding foods containing high levels of purine (the chemical involved in the production of uric acid), such as red meat, offal, oily fish, seafood and foods containing yeast
- avoiding sugary drinks and snacks – these are associated with an increased risk of gout
- maintaining a healthy weight – follow a balanced diet
- taking regular exercise – try activities that don’t put too much strain on your joints, such as swimming
- drinking plenty of water – keeping yourself well hydrated will reduce the risk of crystals forming in your joints
- cutting down on alcohol – avoid beer and spirits in particular and don’t binge drink
9. Hemophilia
This is an inherited medical condition where the blood does not clot properly, leading to internal bleeding and joint damage. When this happens behind the knee, it might cause swelling and inflammation. This causes pain in the knee and calf.
The main treatment for hemophilia is replacement therapy. Concentrates of clotting factor viii (for hemophilia A) or clotting factor ix (for hemophilia B) are injected into your vein. This infusion help replace the clotting factors that’s missing or low.
10. Lupus
This is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks normal, healthy tissue. This results in symptoms such as inflammation, swelling and damage to joint, skin, kidney, blood, heart and lungs.
No cure exist for lupus. The goal for treatment is to ease the symptoms. Treatment can vary depending on how severe your symptoms are and the part of body affected. This may include:
- anti-inflammatory medications for joint pain and stiffness
- steroid creams for rashes
- corticosteroids to minimize the immune response
- antimalarial drugs for skin and joint problems
- disease modifying drugs or targeted immune system agents for more severe cases.
Ruptured popliteal cyst
Most popliteal cysts are asymptomatic. However, cysts may rupture, resulting in pain and swelling of the leg that could also arise from other diseases, including deep vein thrombosis, lymphedema, cellulitis, and tear of a muscle or tendon. Therefore, it is difficult to diagnose a ruptured popliteal cyst based on only a patient’s history and physical examination.
Popliteal cyst mainly occurs by distention of the semimembranosus-gastrocnemius bursa communicating with the knee joint.
Lump behind knee getting bigger
Lumps caused by cancers may have life-threatening consequences, which depend on the type and stage (extent) of the cancer. Left untreated, lumps due to abscesses or serious infections may lead to widespread infection in the body. Knee lumps and associated symptoms can be due to serious diseases, so failure to seek treatment can result in serious complications and permanent damage.
You need to see your doctor as soon as possible to get treated, to avoid the lump getting bigger. Depending with the cause of the lump, different treatment will be applied.
Lump behind knee no pain
A lump behind the knee might be as a result of many causes. While it is sometimes related to arthritis or other condition causing inflammation to the knees, the cyst itself is usually is painless and harmless. It is a good idea to have your health care provider check it out to be sure.
The cyst may feel like a water-filled balloon. Sometimes, the cyst may break open (rupture), causing pain, swelling, and bruising on the back of the knee and calf. It is important to know whether pain or swelling is caused by a Baker’s cyst or a blood clot.
Lump behind knee with pain
A large cyst may cause some discomfort or stiffness, but there are often no symptoms. There may be a painless or painful swelling behind the knee. The cyst may feel like a water-filled balloon. Sometimes, the cyst may break open (rupture), causing pain, swelling, and bruising on the back of the knee and calf. It is important to know whether pain or swelling is caused by a Baker’s cyst or a blood clot. A blood clot (deep venous thrombosis) can also cause pain, swelling, and bruising on the back of the knee and calf. A blood clot may be dangerous and requires immediate medical attention.
Hard lump behind right knee painful
A hard lump behind your knee might be a symptom of baker’s cyst, it is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of the knee. It’s caused when the tissue behind the knee joint becomes swollen and inflamed. The swelling and inflammation can cause, pain in the knee and calf, a build-up fluid around the knee and at times locking in the knee joint. However, sometimes it might not cause any symptoms other than the fluid swelling behind the knee.
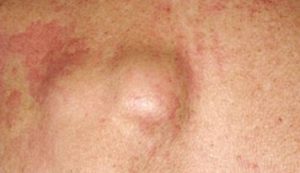
The most effective relief comes from treating the underlying problem. Surgery is at times needed to drain the cyst. In rare cases, the lump can burst (rupture), resulting in fluid leaking down into your calf. This can cause sharp pain, swelling and redness in your calf.
White Lump on side of knee
Lump behind knee is caused by many different ways. A white lump on side of knee might be a symptom of gout, It is caused when the level of uric acid in the blood rise until it becomes excessive (hyperuricemia), causing urate crystals to build up around the joint. The symptoms of gout include painful swelling and inflammation in one or more of the joints. Gout can be extremely painful.
According to the UK Gout Society, gout affects around one in every 100 people. It’s more common in men, particularly those aged 30 to 60, and in older people. Other symptoms of gout include: severe joint pain, swelling and warmth around the joint, red and shiny skin around the joint, mild fever, firm white lumps beneath the skin (which are urate crystals or so-called tophi).
Lump behind knee treatment
Depending with causes of the lump different treatment would be applied. You need to see you health care provider who will assess you and prescribe the best medication possible. The treatment therefore will depend on the causes of the lump, how long you have had the lump and the size of the lump. The most common treatment include:
Treatment for baker’s cyst due to knee cancer depends on the type of cancer, how far it has spread and your general health;
- Surgery, done especially if the cyst is very large or painful and other treatments have not worked. At times a keyhole method is used to close of the connection between the baker’s cyst and the knee joint. The cyst may also be removed at times using open surgery. surgery might help treat an underlying problem for example, repairing a meniscal tear
- Chemotherapy, this is done with medicine to kill the cancer cells, by damaging them so they can’t reproduce and spread. It is used if a cancer has spread or there is a risk that it will.
- Radiotherapy, this is the treatment of cancer involving high-energy radiation. It commonly used to tear the cancer. It would also work to treat other condition such as thyroid disease and some blood disorders.
Treatment for a lump due to lymphoma would include;
- Biologic therapy, this treatment increases your body ability to fight cancer. It does this by giving a boost to your immune system.
- Chemotherapy, this treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells and reduce the size of the cancer tumors. This drugs affect healthy cells and causes side effects like hair loss or mouth sores.
- Radiotherapy, this treatment uses high energy x-rays to kill cancer cells, the treatment often takes place in the part of your body the lymphoma is located.
- Transplant, high doses of chemotherapy destroys the lymphoma cells and your bone marrow, which develops blood cells. To avoid this some immature cells that will grow up into red blood cell, white blood cell and platelets (stem cell) maybe taken before chemotherapy, then translated back into the body. They will then find their way to the bone marrow and restore it
Treatment for baker’s cyst due to gout includes pain relief medication to help you cope with gout attack, as well as medication and lifestyle changes to prevent further attacks. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are usually recommended as the first treatment for gout. They work by reducing pain and inflammation during an attack. NSAIDs used to treat gout include naproxen, diclofenac and etoricoxib.
Baker’s cyst aspiration Video
Further references
- Baker’s Cyst: http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/184714.php
- Behind knee Lump: https://www.healthgrades.com/symptoms/behind-knee-lump
- Baker’s Cyst: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bakers-cyst/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- http://patient.info/health/bakers-cyst-leaflet
- Baker’s Cyst: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bakers-cyst/basics/complications/con-20023332
- Popliteal Cyst: http://www.medicinenet.com/baker_cyst/page3.htm
- http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/tc/bakers-cyst-topic-overview
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
The hormones used in Hormone Replacement Therapy are synthetic hormones,
which means tey are created andd developed in the
lab and aren’t produced naturally by the body.
I beloved as much as you’ll obtain carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you want be delivering the following. ill surely come more in the past again since exactly the same nearly a lot frequently within case you shield this hike.